Shoulder Bursitis Pain: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Acupuncture's Surprising Benefits
- Dr. Scott Martin

- Nov 4, 2024
- 6 min read
Updated: Mar 12, 2025
Shoulder bursitis is a common cause of shoulder pain and stiffness, affecting daily activities and quality of life. Although there are many treatment options, acupuncture has gained popularity for its effectiveness in reducing pain and inflammation associated with this condition. In this article, we’ll break down the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for shoulder bursitis, highlighting scientific evidence supporting acupuncture as a powerful treatment method - there is even a video demonstration on a patient.

Key Takeaways
What is Shoulder Bursitis Pain? Inflammation of the shoulder’s bursa, causing pain and stiffness.
Diagnosis: Physical exams, imaging, and medical history review.
Development: Typically caused by repetitive shoulder movement, trauma, or poor posture.
Treatment Options:
Conservative: Rest, ice, physical therapy.
Medications: NSAIDs, corticosteroid injections.
Acupuncture: Proven to reduce pain, improve circulation, and reduce inflammation.
Scientific Support: Research confirms acupuncture’s effectiveness in reducing shoulder pain and improving mobility.
Prevention Tips: Maintain good posture, strengthen muscles, and avoid repetitive shoulder movements.
For anyone dealing with persistent shoulder pain, exploring acupuncture as part of a holistic treatment plan may offer lasting relief.
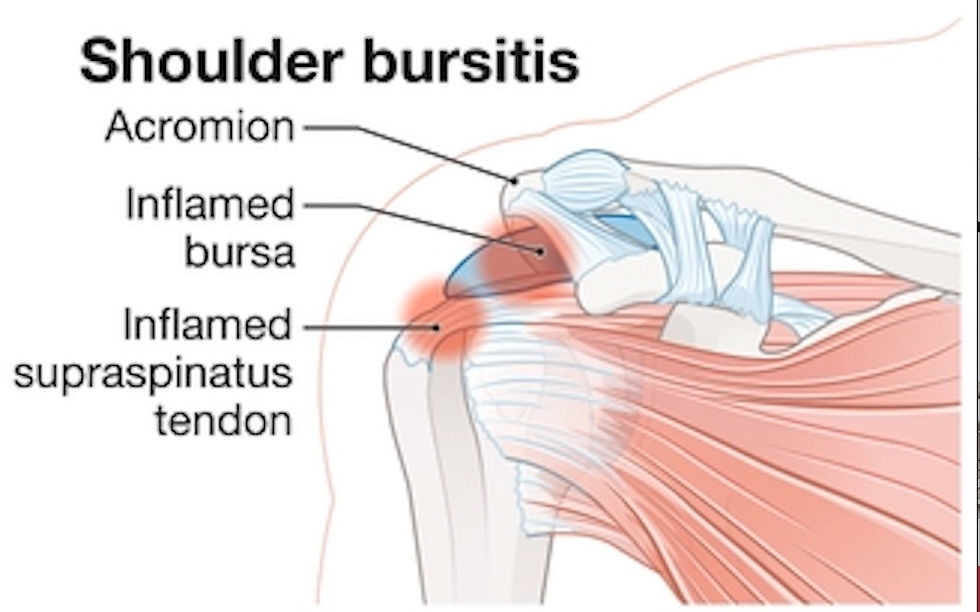
What is Shoulder Bursitis Pain?
Shoulder bursitis occurs when one or more of the bursae in the shoulder become inflamed. Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles around a joint. In the shoulder, these bursae reduce friction between the shoulder blade, rotator cuff, and the upper arm bone.
Causes and Risk Factors
Shoulder bursitis typically results from repetitive motions, injury, or prolonged pressure. Common causes and risk factors include:
Repetitive Activities: Sports, lifting, and other repeated movements that stress the shoulder.
Injury or Trauma: A direct hit or fall onto the shoulder.
Poor Posture: Incorrect posture strains shoulder muscles, increasing friction on the bursa.
Underlying Conditions: Rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and gout may increase the risk.
Differentiating Shoulder Bursitis, Rotator Cuff Tear, and Supraspinatus Tendonitis
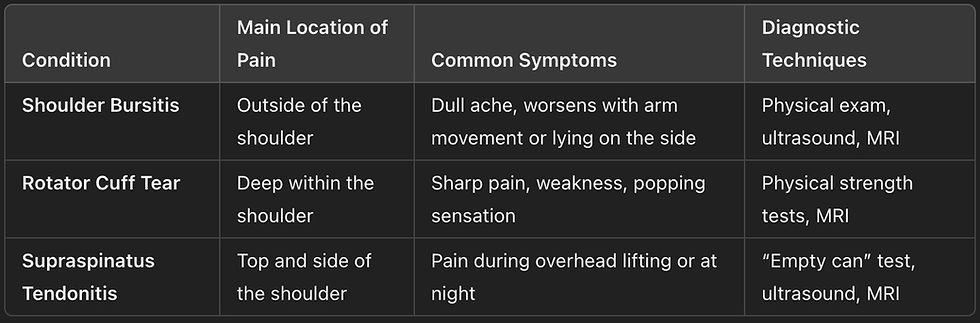
Shoulder pain can stem from various issues, making it challenging to determine the exact cause. Three common sources of shoulder pain include shoulder bursitis, rotator cuff tears, and supraspinatus tendonitis. While they may present with similar symptoms, each condition affects different parts of the shoulder structure and may require different treatments. Here’s how to tell them apart.
1. Shoulder Bursitis
Shoulder bursitis is inflammation of the bursa—a small, fluid-filled sac that cushions the tendons and muscles around the shoulder joint. When the bursa becomes irritated, it swells, causing pain and discomfort.
Symptoms: Dull, aching pain that’s often felt on the outside of the shoulder. Pain may worsen with movement, particularly when raising the arm overhead or lying on the affected shoulder. Swelling and tenderness around the shoulder are also common.
Diagnosis: Physical exams focus on locating the pain and evaluating shoulder movement limitations. Imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI may show inflammation or fluid around the bursa.
2. Rotator Cuff Tear
The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder. A rotator cuff tear happens when one of these tendons is damaged, often from overuse, trauma, or age-related degeneration.
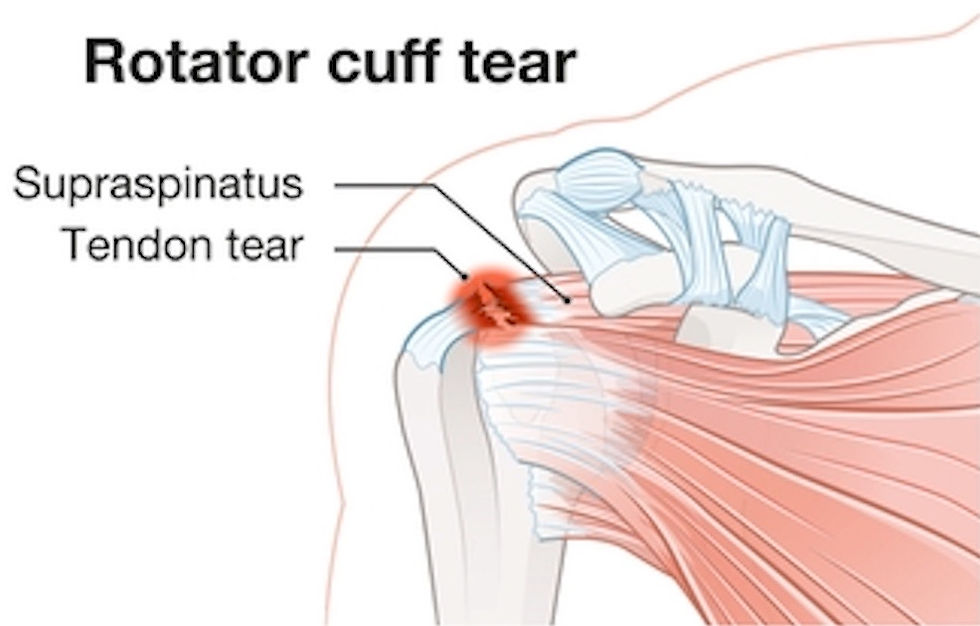
Symptoms: Sharp, intense pain, especially when lifting or rotating the arm. Weakness in the shoulder may make it difficult to lift objects or perform simple tasks. Patients may feel a popping sensation during movement and often have trouble sleeping on the affected shoulder.
Diagnosis: A physical examination will typically reveal weakness in the shoulder, especially in specific arm movements. Imaging tests, particularly MRI, are essential to confirm the tear’s location and severity.
3. Supraspinatus Tendonitis
Supraspinatus tendonitis is an inflammation of the supraspinatus tendon, one of the main tendons in the rotator cuff. This tendon passes through a narrow space and is prone to inflammation due to repetitive motion or overuse.
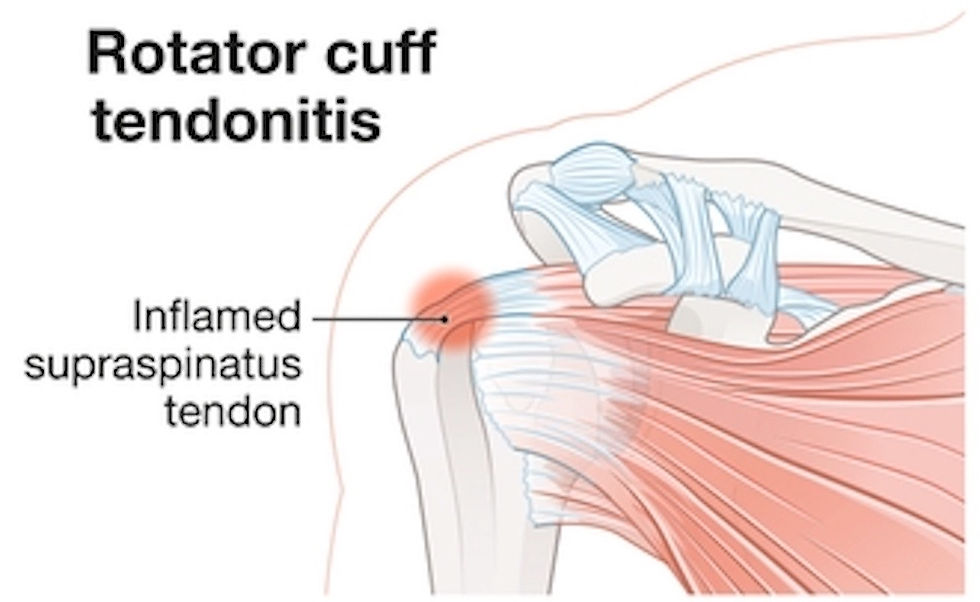
Symptoms: Pain in the upper shoulder area, particularly when lifting the arm sideways or overhead. The pain is often felt at the top and side of the shoulder and may worsen at night.
Diagnosis: A doctor may use the “empty can” test, where the patient holds their arm out as if pouring out a can. Pain during this motion suggests supraspinatus tendonitis. Ultrasound or MRI can also help visualize inflammation in the tendon.
Development of Shoulder Bursitis
Shoulder bursitis develops due to continuous friction or pressure on the bursa, leading to inflammation. Here’s how the condition typically develops:
Friction and Repetition: Repeated or high-intensity shoulder movement causes the bursa to swell.
Chemical Irritation: Friction releases chemicals that irritate the bursa, leading to inflammation.
Structural Imbalance: Muscle imbalances or poor posture can increase strain, worsening bursitis over time.
This irritation triggers pain and stiffness, often limiting shoulder function and strength.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Bursitis
A range of treatments can alleviate shoulder bursitis symptoms, from rest and home care to medical and alternative therapies.
1. Conservative Treatments
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding repetitive shoulder motions and resting the joint.
Ice and Heat: Applying ice to reduce inflammation or heat to relieve muscle stiffness.
Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises to stabilize shoulder muscles and ease joint stress.
2. Medications
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen or naproxen for reducing pain and swelling.
Corticosteroid Injections: A steroid injection into the bursa to reduce severe inflammation and pain.
3. Acupuncture: A Natural Path to Relief
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese therapy, is gaining recognition for its effectiveness in treating shoulder bursitis. This technique involves inserting fine needles into specific points to reduce pain, improve circulation, and restore function.
Pain Relief: Studies indicate that acupuncture releases endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers.
Enhanced Blood Flow: Needling promotes blood flow to the shoulder, supporting healing.
Reduced Inflammation: Acupuncture influences the body’s inflammatory response, decreasing bursa swelling.
This a a video of an acupuncture treatment with commentary by doctor and patient regarding the treatment and effects.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Acupuncture
Research supports shoulder bursitis pain acupuncture treatment as an effective option. A 2017 study in Pain Medicine found that acupuncture significantly reduced shoulder pain and improved mobility in patients with bursitis. Another review in Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies highlights acupuncture's benefits, particularly for those experiencing chronic shoulder pain.
Shoulder Bursitis Pain Acupuncture Treatment: What to Expect
If you’re considering acupuncture, here’s a typical treatment process:
Initial Consultation: The practitioner will discuss your symptoms and determine acupuncture points for treatment.
Session Length: Sessions usually last between 30-60 minutes.
Number of Sessions: Many patients find relief after 3 - 5 sessions, though this varies.
Complementary Techniques: Acupuncturists may use additional therapies like cupping or moxibustion (heat therapy) to enhance results.
Other Alternative Treatments for Shoulder Bursitis
Beyond acupuncture, other alternative therapies may relieve shoulder bursitis symptoms:
Massage Therapy: Massaging shoulder muscles relieves tension and reduces strain on the bursa.
Chiropractic Adjustments: Chiropractors can improve shoulder alignment, reducing joint stress.
Yoga and Stretching: Gentle stretching improves flexibility and strengthens muscles supporting the shoulder.
Osteopathy: treatment is based on the ideas that the body’s structure and function are reciprocally interrelated and the body has the capacity of self-regulation and self-healing.

Preventing Shoulder Bursitis Recurrence
To avoid recurrent bursitis, it’s essential to adopt shoulder-friendly habits. Here are a few tips:
Practice Good Posture: Maintaining proper posture prevents undue stress on shoulder joints.
Strengthen Supporting Muscles: Exercises targeting the shoulder and back muscles provide joint stability.
Modify Repetitive Activities: If your work or hobbies involve repeated shoulder use, take breaks or adjust techniques.
Summary
Shoulder bursitis can be a challenging condition, but with the right approach, you can find relief and prevent future flare-ups. Acupuncture is a promising alternative treatment that offers pain relief and supports shoulder health. Combined with traditional treatments or other therapies, acupuncture can be an effective part of a comprehensive shoulder bursitis treatment plan.



Comments